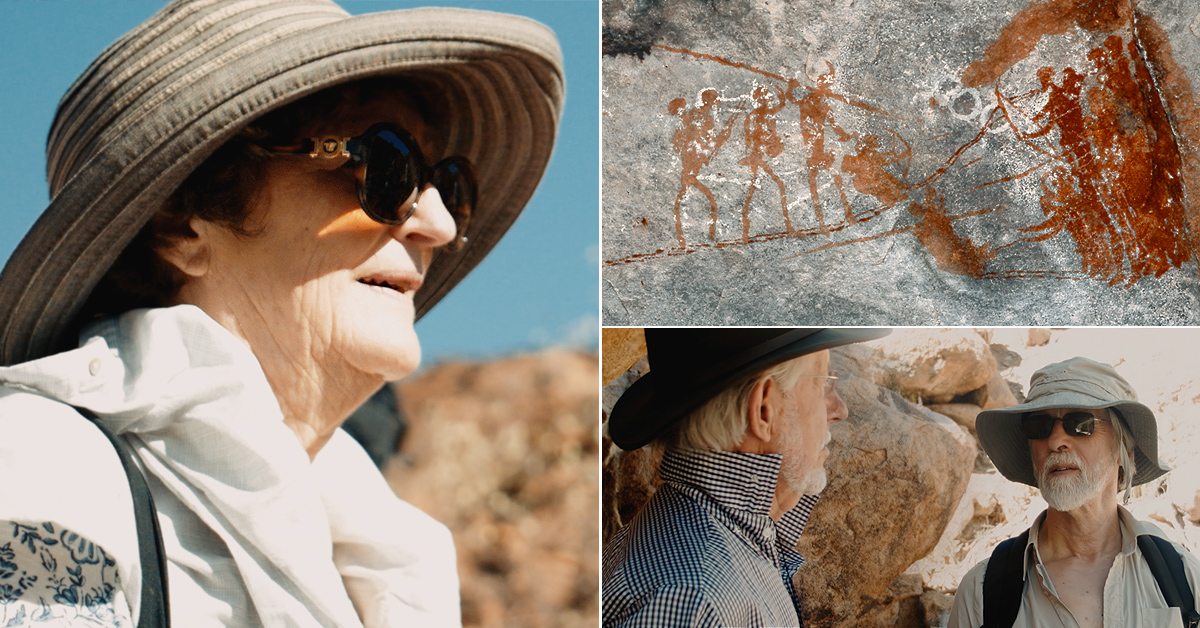
An article by Michael Le Page on newscientist.com - Earliest roasted root vegetables found in 170,000-year-old cave dirt - reports on the charred fragments found in 170,000-year-old ashes in a cave in southern Africa which may represent the earliest roasted root vegetables yet found. The finding suggest the real “paleo diet” included lots of roasted vegetables rich in carbohydrates, similar to modern potatoes.
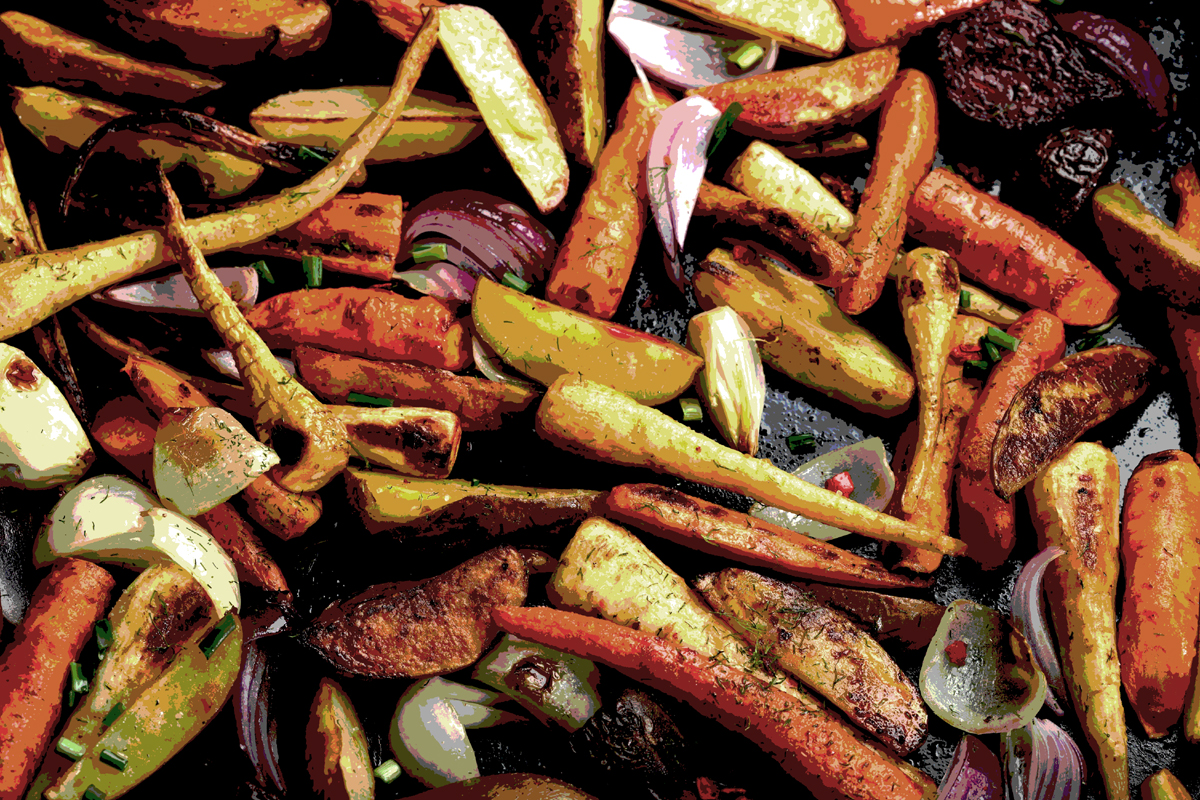

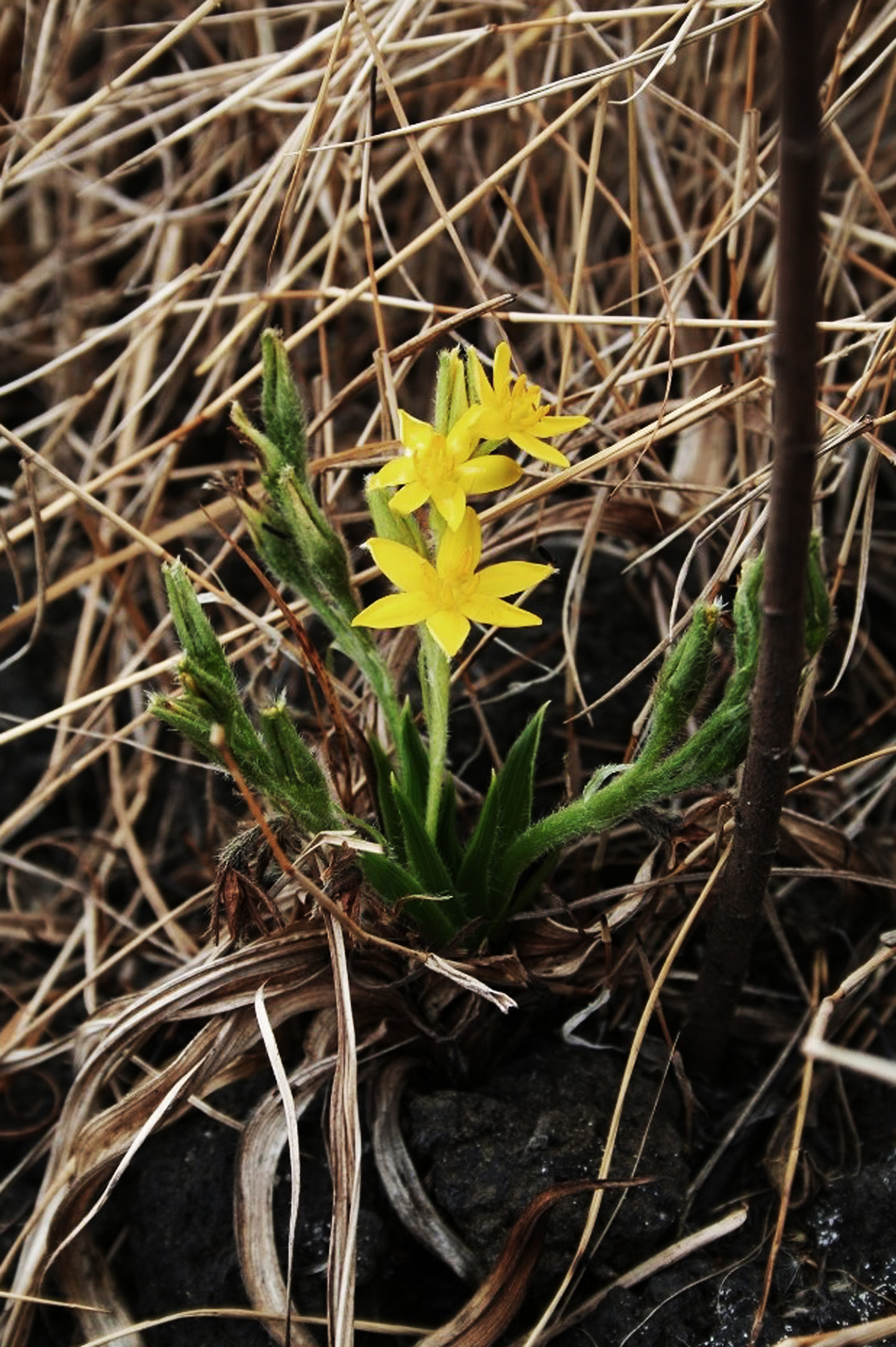
Team leader Lyn Wadley of the University of the Witwatersrand in South Africa explains that “people were eating a very balanced diet, a combination of carbohydrates and proteins.” In 2016, her team found dozens of bits of charcoal in an ash layer in the Border cave in South Africa. This ash layer is the remnant of the fires of early people. By studying the charred remains of hundreds of modern plants under a microscope over the following years, the team were finally able to identify the charcoal fragments as being the rhizomes – subterranean stems – of a plant from the genus Hypoxis.
Seeds of root vegetables and other plants have been found at an 800,000-year-old site in Israel where early humans lived, but Wadley’s find is the earliest clear evidence of roasting. The rhizomes of Hypoxis plants can be as rich in carbohydrates as potatoes, although apparently they taste more like a yam. They are still eaten today, though they have become rare due to overexploitation.

The abundance of the rhizome fragments suggests that roasted root vegetables were a common part of the diet, contrary to the popular notion that early humans ate a lot of meat. Most versions of the paleo diet, which is supposedly based on what our ancestors’ ate, advise people to avoid potatoes as well as grains. Wadley suggests that "the paleo diet is really a misnomer. Our ideas about what early people ate may be skewed by the fact that plant remains are less likely to survive than butchered animal bones – and that researchers seldom look for them. Many archaeologists are not interested in botanical remains.”
While one species of Hypoxis is commonly called the African potato (Hypoxis hemerocallidea), the yellow rhizomes of this plant are bitter, and it is used for medical purposes rather than as food. The Border cave people were probably eating a species with rhizomes with white flesh, such as Hypoxis angustifoli, which is far more palatable.
Journal reference: Science, DOI: 10.1126/science.aaz5926
by Bradshaw Foundation
Tuesday 21 March 2023
by Bradshaw Foundation
Tuesday 07 February 2023
by Bradshaw Foundation
Thursday 19 May 2022
by Bradshaw Foundation
Tuesday 19 October 2021
by Bradshaw Foundation
Friday 25 June 2021
by Bradshaw Foundation
Monday 09 November 2020
by Bradshaw Foundation
Tuesday 03 November 2020
by Bradshaw Foundation
Wednesday 28 October 2020
by Bradshaw Foundation
Tuesday 23 June 2020
by Bradshaw Foundation
Thursday 04 June 2020
by Bradshaw Foundation
Thursday 14 May 2020
by Bradshaw Foundation
Tuesday 12 May 2020
by Bradshaw Foundation
Wednesday 19 February 2020
by Bradshaw Foundation
Tuesday 21 January 2020
by Bradshaw Foundation
Monday 20 January 2020
by Bradshaw Foundation
Thursday 28 November 2019
by Bradshaw Foundation
Tuesday 21 March 2023
by Bradshaw Foundation
Tuesday 07 February 2023
by Bradshaw Foundation
Thursday 19 May 2022
by Bradshaw Foundation
Tuesday 19 October 2021
by Bradshaw Foundation
Friday 25 June 2021
by Bradshaw Foundation
Monday 09 November 2020
by Bradshaw Foundation
Tuesday 03 November 2020
by Bradshaw Foundation
Wednesday 28 October 2020
by Bradshaw Foundation
Tuesday 23 June 2020
by Bradshaw Foundation
Thursday 04 June 2020
by Bradshaw Foundation
Thursday 14 May 2020
by Bradshaw Foundation
Tuesday 12 May 2020
by Bradshaw Foundation
Wednesday 19 February 2020
by Bradshaw Foundation
Tuesday 21 January 2020
by Bradshaw Foundation
Monday 20 January 2020
by Bradshaw Foundation
Thursday 28 November 2019
Friend of the Foundation