An article by Science Correspondent Brian Handwerk on smithsonianmag.com - Oldest Known Neanderthal Engravings Were Sealed in a Cave for 57,000 Years - reports on the Neanderthal art that was created long before modern humans inhabited France’s Loire Valley.
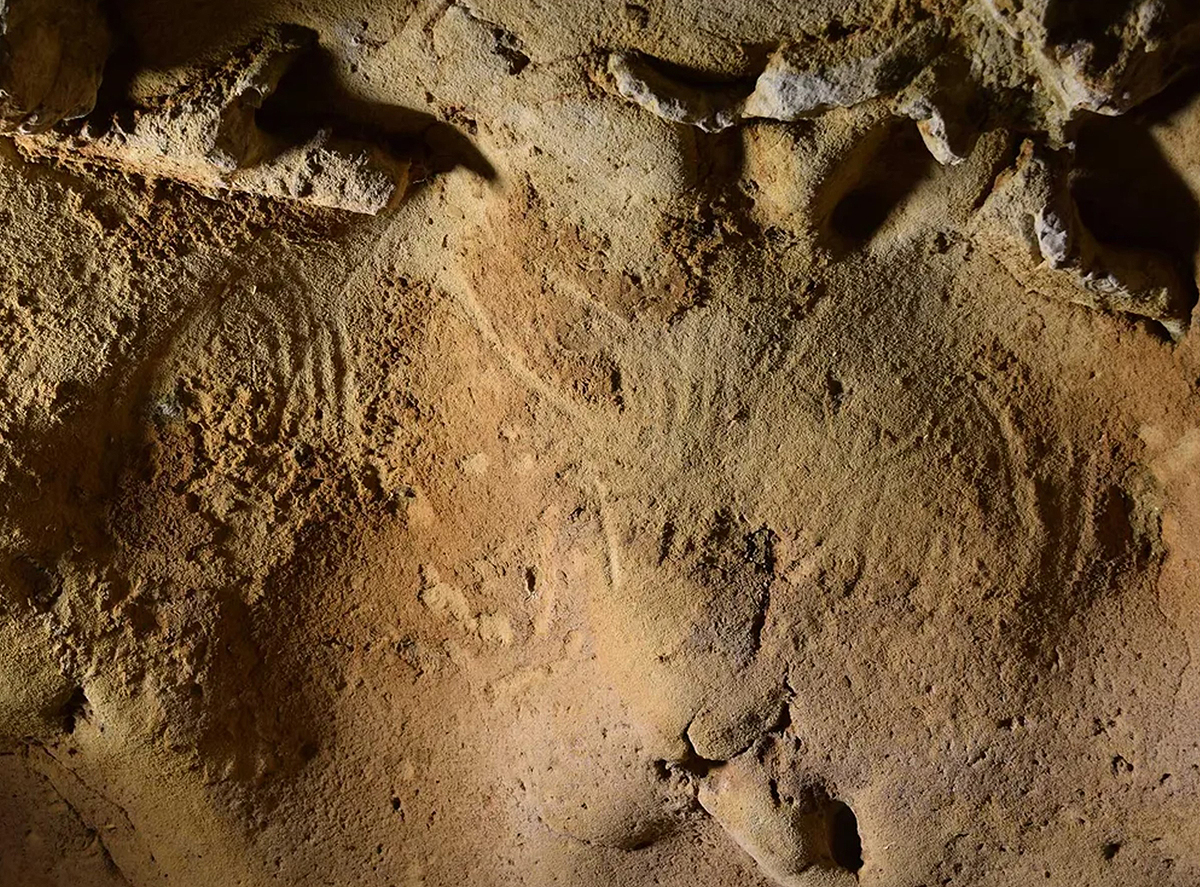

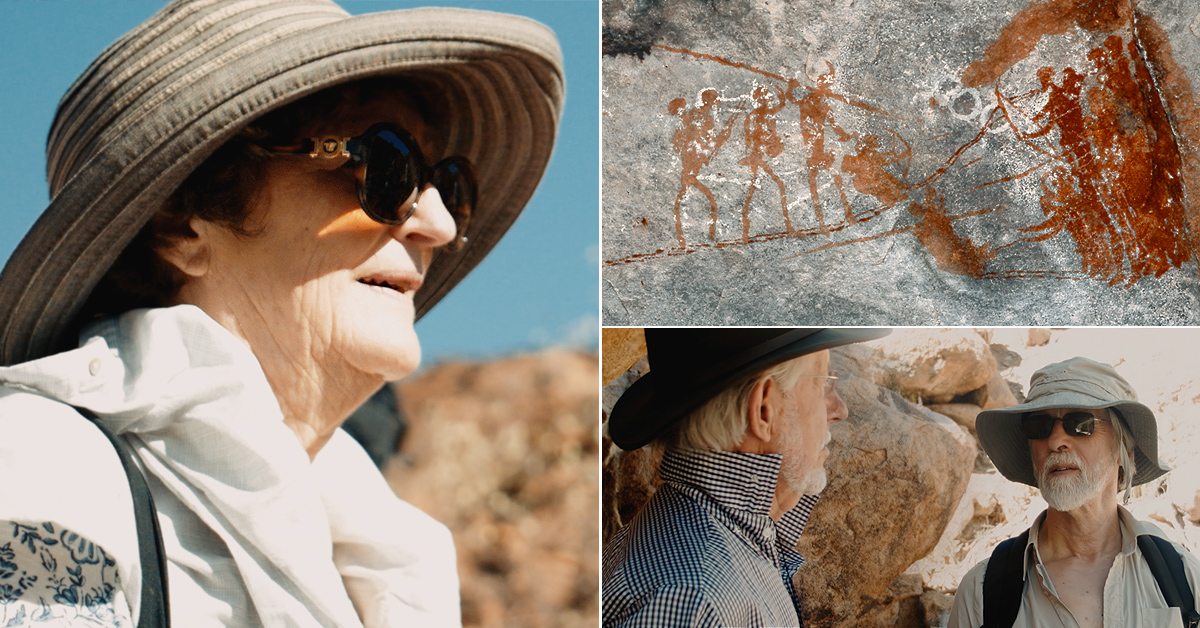
'More than 57,000 years have passed since Paleolithic humans stood before the cave wall, with its soft, chalky rock beckoning like a blank canvas. Their thoughts and intentions are forever unknowable. But by dragging their fingers across the rock and pushing them into the cave wall, these creative cave dwellers deliberately produced enduring lines and dots that would lie hidden beneath the French countryside for tens of thousands of years.'
Scientists have discovered that these significant and intentional patterns are the oldest known example of Neanderthal cave engravings.
Authors of a study published Wednesday in PLOS One analyzed, plotted and 3D modeled the markings and compared them with other wall markings of all types to confirm that they are the organized, intentional products of human hands. The team also dated deep sediment layers that had buried the cave’s opening to reveal that it was sealed up with the engravings inside at least 57,000 and as long as 75,000 years ago — long before Homo sapiens arrived in this part of Europe.
This find, supported by the cave’s array of distinctly Neanderthal stone tools, identifies Neanderthals as the artists.
“For a long time it was thought that Neanderthals were incapable of thinking other than to ensure their subsistence,” notes archaeologist and study co-author Jean-Claude Marquet, of the University of Tours, France. “I think this discovery should lead prehistorians who have doubts about Neanderthal skills to reconsider.”
La Roche-Cotard is an ancient cave nestled on a wooded hillside above the Loire River. It was first uncovered in 1846 when quarries were operated in the area during construction of a railroad line. When it was first excavated in 1912, the array of prehistoric stone implements and cut-marked and charred bones of bison, horses and deer within revealed that Paleolithic hunters had frequented the site many thousands of years earlier.
Scientists first noted the finger tracings as early as the 1970s. Beginning in 2016, the authors of the new study diligently plotted the various distinct panels and created 3D models for comparisons with other known examples of Paleolithic engravings. They also identified the cave’s many other wall markings made by the claws of animals, like cave bears, and by metal or other implements during modern incursions into the cave after 1912. Marquet says this process helped to show that the engraved panels were created in a structured and intentional manner.
The results also suggested that the designs were created by human hands, working the soft chalk wall, a material known as tuffeau, made of fine quartz grains and ancient mollusk shell fragments. The rock is permeable and covered with a fragile sandy-clay film.
“The authors present as convincing a case as can be made from a site disturbed by early excavations that the animal and human marks on its walls were left long before the arrival of our own species in Europe,” says archaeologist Paul Pettitt of Durham University in England, who wasn’t involved with the research. “Given that the cave’s archaeology is exclusively indicative of Neanderthals, with no evidence of subsequent Upper Paleolithic occupation, presumably because the cave was by this time inaccessible, this provides strong indirect, cumulative evidence that Neanderthals produced the finger markings.”
Co-author Eric Robert, an archaeologist at the National Museum of Natural History in Paris, says the graphics are impossible to interpret because they were made by a vanished people for viewing by their contemporaries. He states “These images are not for us, and we do not have the keys to understanding their meaning, their possibly diverse and multiple functions.”
by Bradshaw Foundation
Thursday 29 May 2025
by Bradshaw Foundation
Monday 03 February 2025
by Bradshaw Foundation
Friday 09 August 2024
by Bradshaw Foundation
Wednesday 24 July 2024
by Bradshaw Foundation
Thursday 04 July 2024
by Bradshaw Foundation
Monday 01 July 2024
by Bradshaw Foundation
Wednesday 20 March 2024
by Bradshaw Foundation
Tuesday 13 February 2024
by Bradshaw Foundation
Tuesday 13 February 2024
by Bradshaw Foundation
Thursday 01 February 2024
by Bradshaw Foundation
Tuesday 28 November 2023
by Bradshaw Foundation
Thursday 23 November 2023
by Bradshaw Foundation
Monday 20 November 2023
by Bradshaw Foundation
Tuesday 31 October 2023
by Bradshaw Foundation
Thursday 26 October 2023
by Bradshaw Foundation
Wednesday 20 September 2023
by Bradshaw Foundation
Thursday 29 May 2025
by Bradshaw Foundation
Monday 03 February 2025
by Bradshaw Foundation
Friday 09 August 2024
by Bradshaw Foundation
Wednesday 24 July 2024
by Bradshaw Foundation
Thursday 04 July 2024
by Bradshaw Foundation
Monday 01 July 2024
by Bradshaw Foundation
Wednesday 20 March 2024
by Bradshaw Foundation
Tuesday 13 February 2024
by Bradshaw Foundation
Tuesday 13 February 2024
by Bradshaw Foundation
Thursday 01 February 2024
by Bradshaw Foundation
Tuesday 28 November 2023
by Bradshaw Foundation
Thursday 23 November 2023
by Bradshaw Foundation
Monday 20 November 2023
by Bradshaw Foundation
Tuesday 31 October 2023
by Bradshaw Foundation
Thursday 26 October 2023
by Bradshaw Foundation
Wednesday 20 September 2023
Friend of the Foundation